1.Overview
kobject、ktype、kset作为统一设备模型的基础,目的是为了抽象出基类操作。内核中driver、device、bus结构都继承这个struct。例如,每个内核对象都需要有引用计数,都需要维护sysfs下的文件层级关系,那没必要每个对象都各自实现这个方法,每个设备都包含一个kobject就可以了。
kset则是一系列的kobject的组合,很多内核对象有各种各样的相关性,共同特点。那我们都可以把他们归属为同一个kset组合。例如在devices_init时,创建的device_kset,后续所有注册到内核的设备都属于这个kset。buses_init时创建的bus_kset。所有的bus都属于bus_kset。kset内部也嵌入了struct list_head,用以将kset下所有的kobj连起来。
ktype(struct kobj_type)则是描述了kobject的属性操作方法,例如在kobject释放时候的release函数,kobject在sysfs下的属性接口。
这里也是内核最能体现面向对象的地方。内核采用C语言编写,本不能像C++、Java一样实现继承。但内核开发者很巧妙的运用了指针和结构实现了这一特性。
2.kobj数据结构和三者之间的关系
2.1 kobject、kset、ktype数据结构
struct kobject {
/* kobject 名称 */
const char *name;
/* 链表节点,如果当前kobj从属于某个kset,就会把此节点加入到kset的链表中*/
struct list_head entry;
/* 指向kobj 的父结构 */
struct kobject *parent;
/* 指向当前kobj从属的kset集合 */
struct kset *kset;
/* 指示kobject的属性操作方法 */
const struct kobj_type *ktype;
/* 通过此字段 将kobj和sysfs联合起来 */
struct kernfs_node *sd; /* sysfs directory entry */
/* kobj的引用计数, 如果引用计数位0,则调用注册的release程序,类似于CPP的析构函数 */
struct kref kref;
/* kobj的状态标志位 */
unsigned int state_initialized:1; //初始化状态标志位
unsigned int state_in_sysfs:1; //是否加入到sysfs
unsigned int state_add_uevent_sent:1; //添加kobject的uevent是否发送标志位
unsigned int state_remove_uevent_sent:1; //删除kobject的uevent是否发送标志位
unsigned int uevent_suppress:1; //是否忽略上报uevent
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_KOBJECT_RELEASE
struct delayed_work release;
#endif
};struct kset {
struct list_head list; //链表节点,将kset集合下的所有kobj串起来
spinlock_t list_lock; //自旋锁
struct kobject kobj; //kset自己的内核对象描述,作为kset集合中所有kobj的父obj
const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops; //kset uevent的属性操作方法
} __randomize_layout;struct kobj_type {
void (*release)(struct kobject *kobj); //类似于C++的析构函数,在释放kobj的时候自动调用
const struct sysfs_ops *sysfs_ops; //kobj在/sysfs下的属性操作方法
const struct attribute_group **default_groups; //声明一组属性
//下面的暂时不分析
const struct kobj_ns_type_operations *(*child_ns_type)(struct kobject *kobj);
const void *(*namespace)(struct kobject *kobj);
void (*get_ownership)(struct kobject *kobj, kuid_t *uid, kgid_t *gid);
};2.1 kobject、kset、ktype关系图

3.demo test
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
#include <linux/kobject.h>
struct mizar_kobj{
char *name;
struct kobject kobj; //kobj一般是嵌入到某个数据结构的,例如struct device、struct bus_type
};
struct kset *mizar_kset;
struct mizar_kobj *akobj;
struct mizar_kobj *bkobj;
/*属性及其方法的实现*/
static ssize_t name_attr_show(struct kobject * kobj, struct kobj_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
pr_info("%s[%d]: %s\n", __func__, __LINE__, buf);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t name_attr_store(struct kobject * kobj, struct kobj_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t len)
{
pr_info("%s[%d]: %s\n", __func__, __LINE__, buf);
return len;
}
static ssize_t misc_attr_show(struct kobject * kobj, struct kobj_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
pr_info("%s[%d]: %s\n", __func__, __LINE__, buf);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t misc_attr_store(struct kobject * kobj, struct kobj_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t len)
{
pr_info("%s[%d]: %s\n", __func__, __LINE__, buf);
return len;
}
static struct kobj_attribute name = __ATTR(name,0660,name_attr_show,name_attr_store);
static struct kobj_attribute misc = __ATTR(misc,0660,misc_attr_show,misc_attr_store);
static struct attribute *kobj_attrs[] = {
&name.attr,
&misc.attr,
NULL,
};
struct attribute_group __mizar_kobj_attr_grp = {
.name = "mizar_kobj_attr",
.attrs = kobj_attrs,
};
/*container_of, 内核的又一智慧体现*/
#define to_mizar_kobj(x) container_of(x, struct mizar_kobj, kobj)
/*release函数*/
static void mizar_kobj_release(struct kobject *kobj)
{
struct mizar_kobj *mkobj = to_mizar_kobj(kobj);
pr_info("%s[%d]: %s\n", __func__, __LINE__, kobj->name);
if (mkobj->name)
kfree(mkobj->name);
if (mkobj)
kfree(mkobj);
}
#define to_kobj_attr(x) container_of(x, struct kobj_attribute, attr)
static ssize_t kobj_sysfs_show(struct kobject * kobj, struct attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
struct kobj_attribute *attribute;
attribute = to_kobj_attr(attr);
if (!attribute->show) {
pr_info("%s[%d]: %s unregister\n", __func__, __LINE__, kobj->name);
return -EIO;
}
pr_info("%s[%d]: %s\n", __func__, __LINE__, buf);
/*读写相关的属性文件,先执行sysfs的方法,从这里调用attr的读写方法*/
return attribute->show(kobj, attribute, buf);
}
static ssize_t kobj_sysfs_store(struct kobject * kobj, struct attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t len)
{
struct kobj_attribute *attribute;
attribute = to_kobj_attr(attr);
if (!attribute->show) {
pr_info("%s[%d]: %s unregister\n", __func__, __LINE__, kobj->name);
return -EIO;
}
pr_info("%s[%d]: %s\n", __func__, __LINE__, buf);
return attribute->store(kobj, attribute, buf, len);
}
/*sysfs操作接口实现,类似于file_operation的read和write*/
static struct sysfs_ops __mizar_kobj_sysfs_ops = {
.show = kobj_sysfs_show,
.store = kobj_sysfs_store,
};
/*包含一个release函数,和一个 sysfs接口*/
static struct kobj_type __ktype = {
.release = mizar_kobj_release,
.sysfs_ops = &__mizar_kobj_sysfs_ops,
};
static struct mizar_kobj *create_kobject(const char *name, struct kobject *parent)
{
int ret;
struct mizar_kobj *mkobj;
pr_info("%s[%d]: %s\n", __func__, __LINE__, name);
//为mizar_kobj申请内存
mkobj = kzalloc(sizeof(struct mizar_kobj), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!mkobj)
return NULL;
//为name申请内存
mkobj->name = kzalloc(strlen(name) + 1, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!mkobj->name) {
goto error_kobj;
}
memcpy((void *)mkobj->name, (void *)name, strlen(name));
//初始化kobject,并指定了其ktype操作方法
kobject_init(&mkobj->kobj, &__ktype);
ret = kobject_add(&mkobj->kobj, parent, "%s", name);
if (ret) {
kobject_put(&mkobj->kobj);
goto error_kobj_add;
}
//创建/sys下的节点目录及属性文件
ret = sysfs_create_group(&mkobj->kobj, &__mizar_kobj_attr_grp);
if (ret) {
sysfs_remove_group(&mkobj->kobj, &__mizar_kobj_attr_grp);
goto error_sysfs_create;
}
goto finish;
error_sysfs_create:
kobject_put(&mkobj->kobj);
error_kobj_add:
kfree(mkobj->name);
error_kobj:
kfree(mkobj);
mkobj = NULL;
finish:
return mkobj;
}
static void destory_kobject(struct mizar_kobj *mkobj)
{
sysfs_remove_group(&mkobj->kobj, &__mizar_kobj_attr_grp);
kobject_put(&mkobj->kobj);
kfree(mkobj->name);
kfree(mkobj);
}
/**********************kset 的init和deinit 接口****************************************/
static struct kset *create_kset(const char *name)
{
struct kset *kset;
pr_info("%s[%d]: create kset: %s\n", __func__, __LINE__, name);
kset = kset_create_and_add(name, NULL, NULL); //动态创建一个kset
if (!kset) {
return NULL;
}
return kset;
}
static void destory_kset(struct kset *kset)
{
if (kset)
kset_unregister(kset);
}
/************************************************************************************/
static int kobj_init(void)
{
pr_info("%s[%d]:\n", __func__, __LINE__);
mizar_kset = create_kset("mizar_kset");
if (!mizar_kset)
return -1;
akobj = create_kobject("akobj", &mizar_kset->kobj);
if (!akobj)
return -2;
bkobj = create_kobject("bkobj", &mizar_kset->kobj);
if (!bkobj)
return -3;
return 0;
}
static void kobj_exit(void)
{
pr_info("%s[%d]:\n", __func__, __LINE__);
destory_kobject(akobj);
destory_kobject(bkobj);
destory_kset(mizar_kset);
}
module_init(kobj_init);
module_exit(kobj_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
MODULE_AUTHOR("Mizar.Hou");demo实现了一个
kset:mizar_kset,以及两个kobject:akobj和bkobj,这两个kobj都属于mizar_kset,在/sys路径下直接体现为: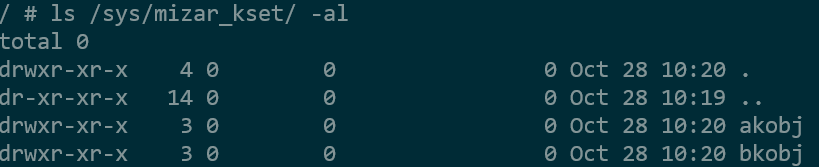
两个
kobject都有相同的kobj_type, 参考struct kobj_type __ktype, 实现了一个release接口,在kobject->kref引用计数减到0的时候,由系统自己调用;包含一对sysfs操作方法,参考__mizar_kobj_sysfs_ops两个
kobject都包含相同的attribute, 在创建kobject时,通过sysfs_create_group(&mkobj->kobj, &__mizar_kobj_attr_grp)创建,直接体现为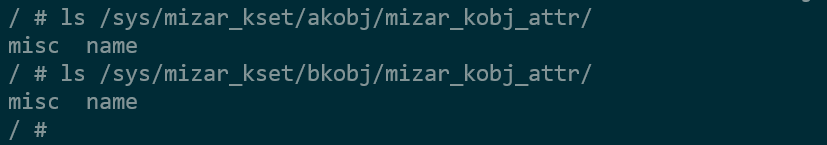
__mizar_kobj_attr_grp包含两个属性,参考struct attribute_group __mizar_kobj_attr_grp的实现,这两个attr的可以在shell中通过cat & echo命令进行读写: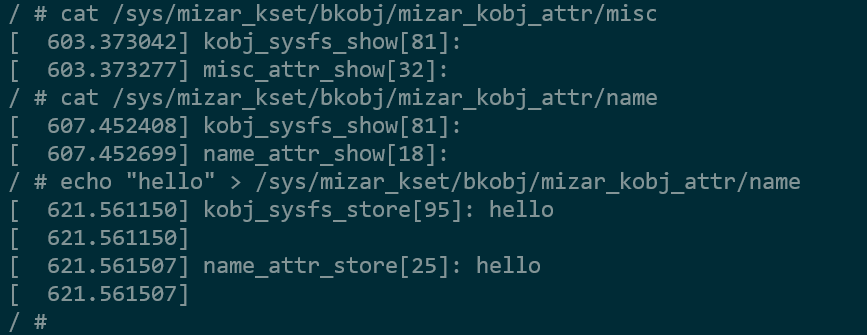
- 通过执行
log可以看出,应用层读写先调用到sysfs的读写操作方法,在调用属性实现的读写方法,从syfs_ops->show到attr->show的调用实现参考kobj_sysfs_show,cat指令如何调用的sysfs的这部分暂时不进行分析。
- 通过执行
使用
rmmod卸载ko, 可以看出在sys下创建的节点已经被删除,同时调用了__ktype中实现的release接口,释放kobject,但是kset中也包含一个kobject,什么事件release的呢? 这是因为初始化kset采用的kset_create_and_add接口中,指定了一个默认的__dynamic_kobj_ktype,在kset_unregister的时候自行release.有兴趣的同学可以使用ftrace跟踪下函数的调用栈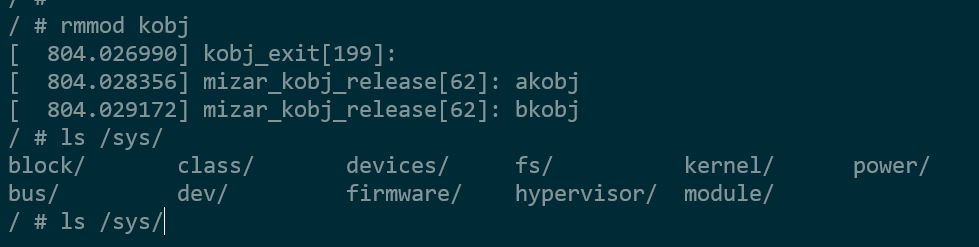
4.kobject 代码走读
文件位置: ${KERNEL_DIRKERNEL_DIR}/lib/kobject.c
4.1 kobject_init
static void kobject_init_internal(struct kobject *kobj)
{
if (!kobj)
return;
kref_init(&kobj->kref); //初始化的时候,kref设置为1
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&kobj->entry);
kobj->state_in_sysfs = 0;
kobj->state_add_uevent_sent = 0;
kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent = 0;
kobj->state_initialized = 1;
}
void kobject_init(struct kobject *kobj, const struct kobj_type *ktype) //初始化kobject的数据结构
{
char *err_str;
......
kobject_init_internal(kobj);
kobj->ktype = ktype;
return;
......
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kobject_init);
4.2 kobject_add
int kobject_set_name_vargs(struct kobject *kobj, const char *fmt,
va_list vargs)
{
const char *s;
if (kobj->name && !fmt)
return 0;
s = kvasprintf_const(GFP_KERNEL, fmt, vargs); //为s申请内存,并将参数传递的字符串保存到s,s就是kobj的name
if (!s)
return -ENOMEM;
if (strchr(s, '/')) { //name中不能有'/',如果有的话,使用'!'代替
char *t;
t = kstrdup(s, GFP_KERNEL);
kfree_const(s);
if (!t)
return -ENOMEM;
strreplace(t, '/', '!');
s = t;
}
kfree_const(kobj->name);
kobj->name = s;
return 0;
}
static __printf(3, 0) int kobject_add_varg(struct kobject *kobj,
struct kobject *parent,
const char *fmt, va_list vargs)
{
int retval;
retval = kobject_set_name_vargs(kobj, fmt, vargs); //设置kobj的name
......
kobj->parent = parent;
return kobject_add_internal(kobj); //将kobj加入/sys
}
int kobject_add(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobject *parent, const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list args;
int retval;
......
va_start(args, fmt);
retval = kobject_add_varg(kobj, parent, fmt, args);
va_end(args);
return retval;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kobject_add);4.2.1 kobject_add_internal
static int kobject_add_internal(struct kobject *kobj)
{
int error = 0;
struct kobject *parent;
......
parent = kobject_get(kobj->parent);
if (kobj->kset) { //如果kobj指定了kset
if (!parent)
parent = kobject_get(&kobj->kset->kobj); //如果kobject没有指定父kobj,则kset->kobject是其父obj
kobj_kset_join(kobj); //将kobj加入kset链表
kobj->parent = parent;
}
error = create_dir(kobj);
if (error) {
......
} else
kobj->state_in_sysfs = 1; //设置标志位,表示kobj已经加入到sysfs
return error;
}4.2.2 create_dir
int sysfs_create_dir_ns(struct kobject *kobj, const void *ns)
{
struct kernfs_node *parent, *kn;
kuid_t uid;
kgid_t gid;
//kobject节点在/sys下的层级关系,如果有父obj,则kobject的目录建在父obj下面,如果没有父obj,直接在/sys下建立新目录
if (kobj->parent)
parent = kobj->parent->sd;
else
parent = sysfs_root_kn;
......
kobject_get_ownership(kobj, &uid, &gid);
//创建目录,名称就是kobj的name,权限755
kn = kernfs_create_dir_ns(parent, kobject_name(kobj), 0755, uid, gid, kobj, ns);
......
kobj->sd = kn;
return 0;
}
static int create_dir(struct kobject *kobj)
{
const struct kobj_type *ktype = get_ktype(kobj);
const struct kobj_ns_type_operations *ops;
int error;
//创建kobject的在/sys下的目录
error = sysfs_create_dir_ns(kobj, kobject_namespace(kobj));
/*以下暂不分析,上面的demo也没有涉及*/
if (ktype) {
error = sysfs_create_groups(kobj, ktype->default_groups);
......
}
sysfs_get(kobj->sd);
ops = kobj_child_ns_ops(kobj);
if (ops) {
BUG_ON(ops->type <= KOBJ_NS_TYPE_NONE);
BUG_ON(ops->type >= KOBJ_NS_TYPES);
BUG_ON(!kobj_ns_type_registered(ops->type));
sysfs_enable_ns(kobj->sd);
}
return 0;
}4.2.3 kobj_kset_join
static void kobj_kset_join(struct kobject *kobj) //将kobj加入到kset的链表中
{
if (!kobj->kset)
return;
kset_get(kobj->kset);
spin_lock(&kobj->kset->list_lock);
list_add_tail(&kobj->entry, &kobj->kset->list);
spin_unlock(&kobj->kset->list_lock);
}4.2.4 kobject_create_and_add
//没啥讲的, 动态创建kobject, kobject_create_and_add
// = kobject_create + kobject_add
// = kmalloc + kobject_init + kobject_add
static struct kobject *kobject_create(void)
{
struct kobject *kobj;
kobj = kzalloc(sizeof(*kobj), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!kobj)
return NULL;
kobject_init(kobj, &dynamic_kobj_ktype); //不一样的是这个地方,会为kobject指定一个默认的ktype
return kobj;
}
struct kobject *kobject_create_and_add(const char *name, struct kobject *parent)
{
struct kobject *kobj;
int retval;
kobj = kobject_create();
if (!kobj)
return NULL;
retval = kobject_add(kobj, parent, "%s", name);
if (retval) {
pr_warn("%s: kobject_add error: %d\n", __func__, retval);
kobject_put(kobj);
kobj = NULL;
}
return kobj;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(kobject_create_and_add);4.2.5 kobject_put
static void kobject_cleanup(struct kobject *kobj)
{
struct kobject *parent = kobj->parent;
const struct kobj_type *t = get_ktype(kobj);
const char *name = kobj->name;
......
/* remove from sysfs if the caller did not do it */
if (kobj->state_in_sysfs) {
__kobject_del(kobj);
}
......
if (t && t->release) {
t->release(kobj); //调用ktype中的release函数
}
/* free name if we allocated it */
if (name) {
kfree_const(name); //释放name占用的内存
}
kobject_put(parent); //父obj的引用计数减1
}
static void kobject_release(struct kref *kref)
{
struct kobject *kobj = container_of(kref, struct kobject, kref);
kobject_cleanup(kobj);
}
void kobject_put(struct kobject *kobj)
{
if (kobj) {
......
kref_put(&kobj->kref, kobject_release);
}
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kobject_put);小结:
kobject的初始化共分成两部分,一是将初始化kobject数据结构,二是为kobject在/sys路径下创建目录节点和属性文件kref引用计数会直接设置为1,在释放kobj的时候,调用kobject_put,在引用计数减到zero时,调用ktype的release函数- 如果
kobject指定了kset,会将kobject加入kset链表 - 如果
kobject有父obj,则目录节点会创建在父目录下,否则直接在/sys路径下创建目录节点
4.2.6 kset_create_and_add
static struct kset *kset_create(const char *name, const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops, struct kobject *parent_kobj)
{
struct kset *kset;
int retval;
kset = kzalloc(sizeof(*kset), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!kset)
return NULL;
retval = kobject_set_name(&kset->kobj, "%s", name);
kset->uevent_ops = uevent_ops;
kset->kobj.parent = parent_kobj;
kset->kobj.ktype = &kset_ktype;
kset->kobj.kset = NULL;
return kset;
}
struct kset *kset_create_and_add(const char *name, const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops, struct kobject *parent_kobj)
{
struct kset *kset;
int error;
kset = kset_create(name, uevent_ops, parent_kobj);
if (!kset)
return NULL;
error = kset_register(kset);
if (error) {
kfree(kset);
return NULL;
}
return kset;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(kset_create_and_add);4.2.7 kset_register
void kset_init(struct kset *k)
{
kobject_init_internal(&k->kobj);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&k->list);
spin_lock_init(&k->list_lock);
}
int kset_register(struct kset *k)
{
int err;
kset_init(k);
err = kobject_add_internal(&k->kobj);
kobject_uevent(&k->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kset_register);5. 参考文献
1. 关于kobjects、ksets和ktypes的一切你没想过需要了解的东西 — The Linux Kernel documentation
2. kobject / kset / ktype(linux kernel 中的面向对象) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
3. 统一设备模型:kobj、kset分析 (wowotech.net)
作者:Mizar.Hou
链接:https://www.mizar.world/linux-driver-model-1
本文采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 进行许可。